Cyber Threat hunting is the proactive process of looking for undiscovered cyberthreats within a network. To locate hostile individuals in your environment who have evaded your initial endpoint security measures, cyber threat hunting investigates deeply. An attacker can enter a network secretly and stay there for months while they gather information, search for sensitive information, or get login credentials that will let them move laterally throughout the system. Because many businesses lack the advanced detection skills necessary to prevent advanced persistent threats from remaining in the network after an adversary has successfully evaded detection and an assault has breached the organization’s defenses.
Table of Contents
Role of Threat Hunting in Enterprise Security?
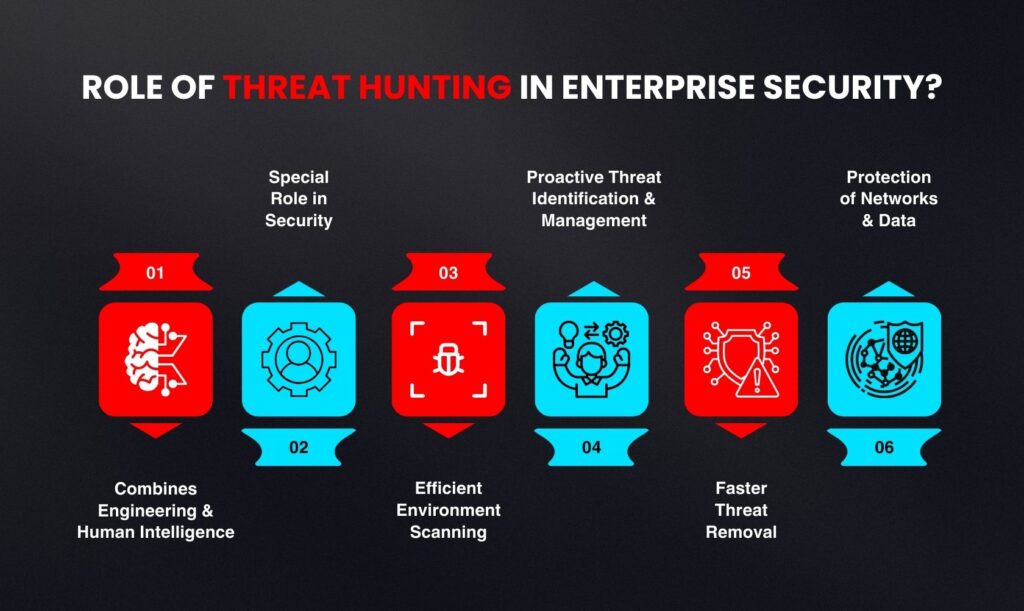
cyber threat hunting combines engineering and human intelligence to look for indications of compromise (IOCs), it serves a special role in enterprise security. Threat intelligence analysts can more effectively scan an organization’s environment and filter out events that need more thorough examination by utilizing the IOC search procedure. The proactive identification and management of hidden dangers is made possible by this threat hunting methodology, which also increases threat detection accuracy and reduces event risk. Threats can be removed more quickly if they are identified and reported to an incident responder, protecting networks and data.
Cyber Threat Hunting Key Steps
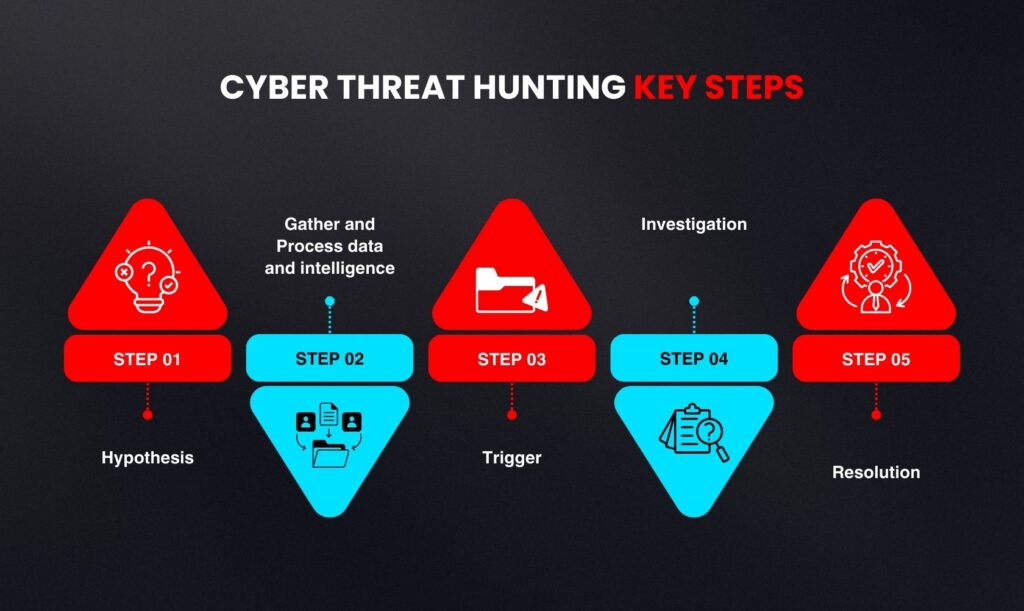
Hypothesis
Any successful threat hunting program starts with identifying the risks that your company is most likely to encounter. This means being aware of the kinds of attacks that have previously been employed against comparable organizations as well as the weaknesses that attackers are most likely to take advantage of. Hunting what you don’t know about is impossible. Numerous sources, including as vulnerability scans, log data, and cyber threat intelligence feeds, can provide this information.
Threat hunting finds unidentified dangers to the cybersecurity of a company. Threat hunters require a beginning point for their investigations in the absence of a known attack or specific threat to look into.
Gather and Process data and intelligence
To discover potential threats to an organization’s systems, the second phase involves organizing and analyzing threat intelligence and high-quality data. Network traffic logs (which display the websites visited), system log files (which document the activities of software programs operating within your firewall at any given time), malware analysis reports (which are produced when researchers discover compromised machines worldwide due to improper patching practices), and even social media posts are some of the various sources of intelligence.
The threat hunter can find data sources that could support or refute the hypothesis and a plan for gathering and evaluating that evidence based on their understanding of the possible threat.
Also read Top 10 cyber security threats
Trigger
Finding a potential threat is only the first step. Finding out if that threat is present on your network and taking appropriate action to neutralize it is the next step. This requires configuring “trigger events,” which are particular circumstances that, when satisfied, signal the likelihood of a danger appearing on the network. Finding undiscovered risks before they have a chance to do significant harm is the aim of threat hunting. In order to do this, you need data and analysis from every department in your company.
Investigation
if a trigger event takes place. The investigation’s objective is to determine the incident’s details and scope in order to facilitate its remediation. A variety of solutions, as well as internal and external data sources, should be included in the investigation, which entails examining all of the data gathered in step 2 as well as any additional data that has since been gathered. Threat hunters should seek for stolen data or other information about the attack on dark web marketplaces in addition to looking for indications of infection on corporate systems.
Resolution
Taking action to address the issue is the last phase in the cyber threat hunting process. To decide on the appropriate course of action, this involves working together with the pertinent teams within the company.
The resolution could involve anything from putting new security controls in place to pursuing legal action against the intruders, depending on how serious the event was. An in-depth understanding of what happened and the best way to defend the organization from similar attacks in the future should be the end result. When an incident happens, the investigation process makes sure your company has all the information it needs to take the necessary steps to stop major delay or harm from happening again.
Cyber Threat Hunting Methods

Threat hunting is a strategic cybersecurity technique that assists companies in identifying and eliminating risks before they have a chance to do damage. Security teams can find weaknesses, boost defenses, and unearth concealed assaults by employing several approaches. The most successful strategies employed by experts include the following.
Hypotheses- Driven Threat hunting
This approach begins with the creation of a hypothesis based on threat actor knowledge, historical assault trends, and intelligence. After making predictions about the potential attack vectors, security analysts examine network activity, logs, and endpoints to confirm or disprove the theory. This method is very proactive and frequently identifies risks that automated tools overlook. It makes hunting more strategic and focused by enabling security teams to concentrate on particular areas of concern rather than conducting a blind search.
Threats Hunting using IOCs and IOAs
This method focuses on identifying Indicators of Attack (IOAs) that signify persistent malicious behavior as well as Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), such as suspicious IP addresses, malicious file hashes, or known hacked domains. Whereas IOAs offer information about ongoing or possible attacks, IOCs highlight breaches that have already taken place. By keeping an eye on these indicators, analysts can identify the attack path, isolate compromised systems, and take immediate steps to stop the threat from spreading.
Visit what is threat hunting?
Analytics-Driven Threat Hunting
To identify odd or suspicious trends, analytics-driven hunting makes use of behavioral monitoring, machine learning models, and extensive data analysis. This technique can identify abnormalities that deviate from predetermined baselines by examining network traffic, endpoint activity, and historical logs. Because of this, it is effective against zero-day attacks and advanced persistent threats (APTs). It’s a very scalable method that continuously improves detection skills as it consumes more data over time.
Hunting Using the MITRE ATT&CK Framework
An internationally known, systematic database of attacker tactics, methods, and procedures (TTPs) is provided via the MITRE ATT&CK platform. It is used by security teams to map the behavior of adversaries and determine which approaches might have been employed in an attack. Organizations can enhance incident response plans, find coverage holes in their defenses, and gain a better understanding of attack evolution by coordinating threat-hunting operations with the framework. This method guarantees that hunts are methodical, replicable, and based on actual threat intelligence.
What is the relevance of cyber threat hunting?
Finding hidden cyberthreats within a network that might have evaded conventional security measures is known as cyber threat hunting. Attackers can collect credentials or critical data while going months without detection, which makes it crucial. By identifying these hazards early on, threat hunting lowers the possibility of harm.
What are the primary steps in the process of looking for cyber threats?
Hypothesis: Using intelligence and past attack trends to identify potential threats.
Data collection and processing include gathering network traffic information, logs, and other intelligence.
Trigger: Establishing particular parameters to identify potential dangers.
Investigation: Examining all gathered information to verify the existence and extent of the threat.
Resolution: Taking steps like removing the threat or strengthening security measures.
In what ways does analytics-driven threat hunting outperform IOC-based APT detection?
IOC-based detection identifies known threats but overlooks attacks that are novel or changing. Analytics-driven hunting is more effective against APTs and zero-day threats because it use behavior analysis and machine learning to find anomalies without depending on established signs.