Table of Contents
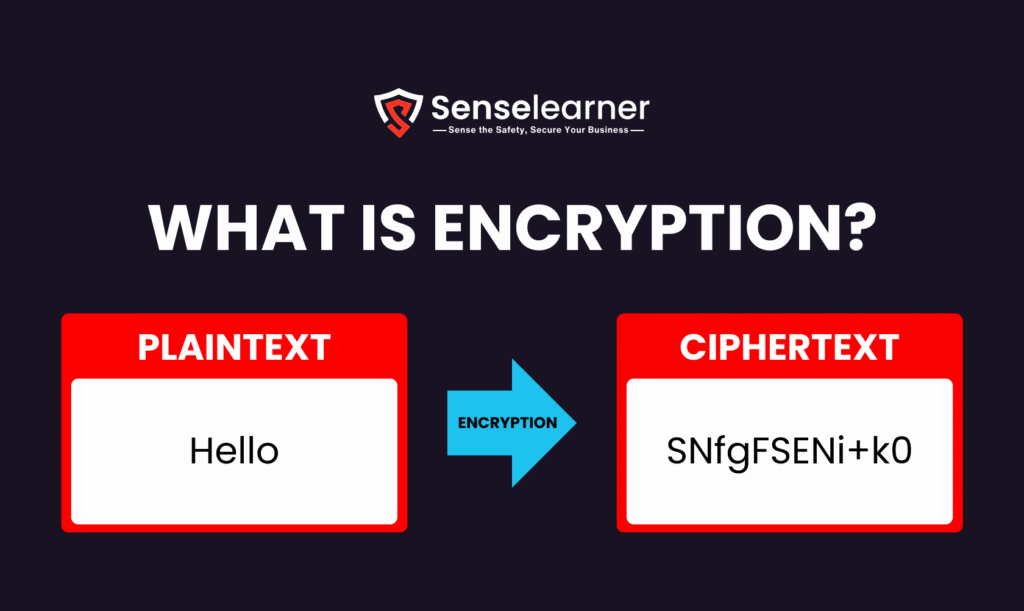
Imagine you want to send a secret message to a friend. You could write it in a special code that only the two of you know. Even if someone else intercepts the message, they’ll just see gibberish and won’t be able to read your secret.
That’s exactly what encryption is! At its heart, encryption is a way of scrambling information so that it can’t be read by anyone except the person who is meant to receive it. It turns plain, readable data (like a message or a credit card number) into a secret code. Think of it as putting a lock on your digital information.
How Encryption works ?
An algorithm, which is a collection of rules, and a key, which is a collection of characters, form the basis of encryption. The key serves as the password to unlock the data, and the algorithm decides how it is scrambled. Consider it as a lock and key, where the key is the particular object that can open the lock and the algorithm is the lock’s design. The encryption becomes more difficult to unlock the longer and more complicated the key.
Types of Encryption?
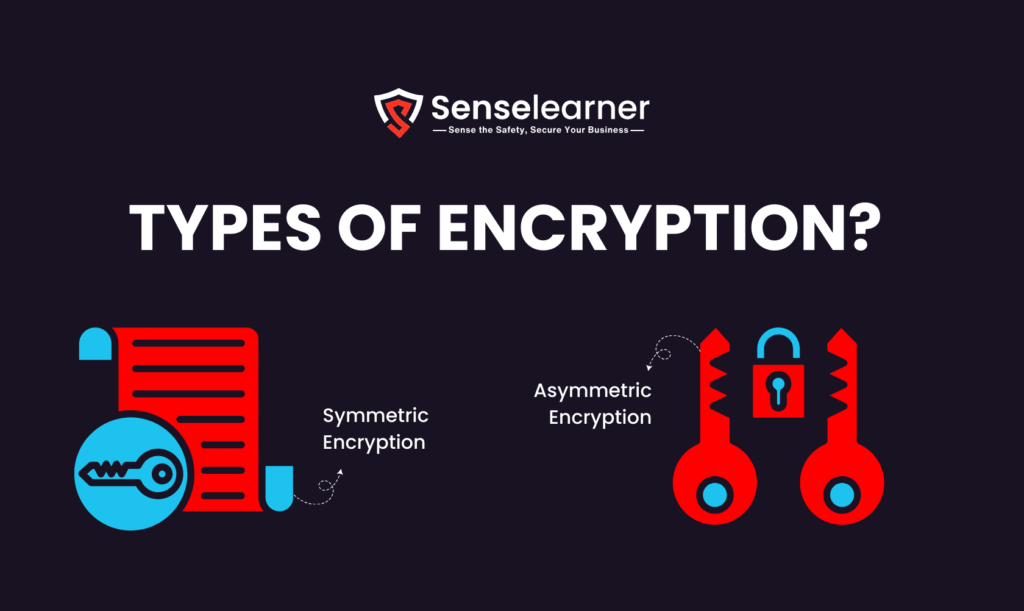
There are mainly two types of Encryption symmetric and asymmetric
1- Symmetric Encryption
In this method, a single, shared key is used for both data encryption and decryption. Because it is quicker and more effective, it is perfect for encrypting big data sets. The largest obstacle, though, is safely giving the recipient the key. For instance, the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm is a symmetric algorithm.
2- Asymmetric Encryption
Public-key cryptography, which is another term for asymmetric encryption, employs a pair of keys: a private key for decryption and a public key for encryption. While the recipient is required to keep the private key confidential, the public key can be freely shared. The matching private key is the only way to decrypt data that has been encrypted using the public key. This resolves the issue of symmetric encryption’s key-sharing.
visit what is Encryption?
Why It’s Important to Encrypt
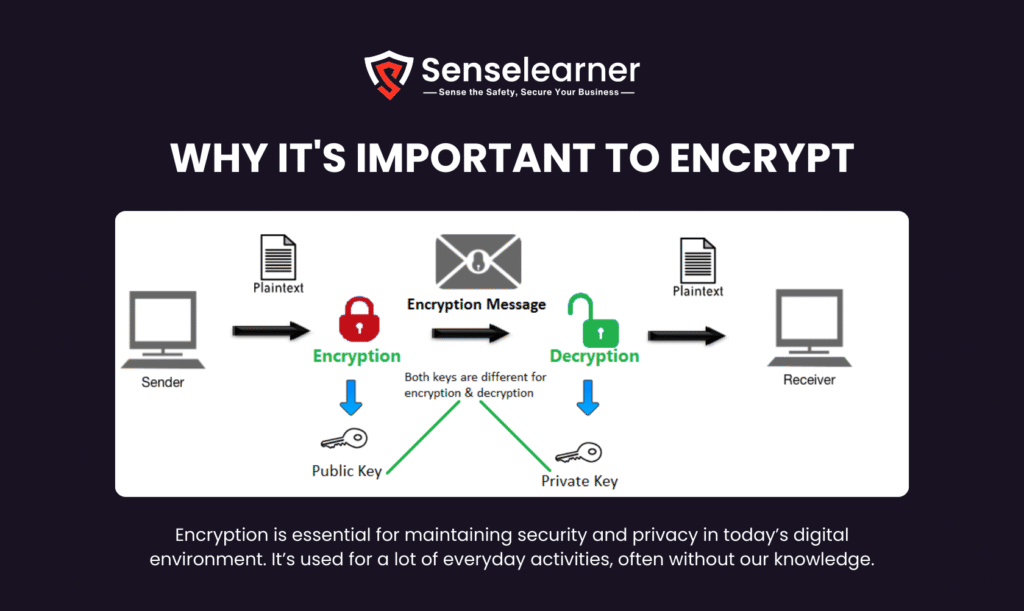
Encryption is essential for maintaining security and privacy in today’s digital environment. It’s used for a lot of everyday activities, often without our knowledge.
Online shopping
To guard against hackers stealing your credit card information, it is encrypted when you make an online purchase. By converting your financial information into unintelligible code that is worthless to hackers even if it is intercepted, this procedure protects your information. Your bank account information and personal data would be transmitted in plain text without this security, making them a prime target for fraud.
Web browsing
A website’s “HTTPS” extension protects your data while it moves between your browser and the website’s server by indicating that the connection is secure and encrypted. This is essential for any website where you enter personal data or log in. A “man-in-the-middle” attack, in which a third party intercepts your data while you are sending and receiving it, is avoided.
How can Encryption ensure the security of online browsing?
By establishing a secure, private connection between your browser and the website you are viewing, encryption helps to make internet browsing more secure. This procedure guarantees that any data transmitted is unreadable by anybody else and is mainly powered by the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. A website that begins with “https://” is utilizing this secure, encrypted connection, as indicated by the “s” in the address.
Read https://senselearner.com/what-is-e-mail-security-audit-and-why-it-matters/
The TLS Handshake: A Secure Introduction
A “TLS handshake” is performed between your browser and the web server prior to any data being transferred. To create a secure channel and authenticate the server, follow these steps.
1 Hello
The server receives a “hello” message from your browser, which initiates the connection and shares the encryption techniques it supports.
2 Certificate Exchange
In response, the server sends its SSL/TLS certificate, which is a digital document that serves as identification proof. The public key for the server is contained in this certificate.
3 Authentication
To make sure the website is authentic and not a scam seeking to steal your information, your browser verifies the certificate with a Certificate Authority, a reliable third party.
4 Key Exchange
Next, the browser and server safely generate a session key by combining symmetric and asymmetric encryption in a clever way. The rest of the conversation will be conducted with this key, which is a shared, temporary secret
The Secure Communication
After the TLS handshake is over, the shared session key is used to encrypt all further data sent back and forth between your browser and the server. This type of symmetric encryption is significantly quicker for data that flows continuously.
Data in Transit
Information is broken down into encrypted text while you send messages, fill out forms, or enter passwords; only the server with the correct session key can decode it.
Protecting from Eavesdropping
This stops “man-in-the-middle” attacks in which an unauthorized person tries to read and intercept your conversations, particularly on public Wi-Fi networks that aren’t safe enough.
What differentiates symmetric encryption from asymmetric encryption?
Asymmetric encryption employs two keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. Symmetric encryption uses a single shared key for both encryption and decryption.
What makes encryption essential to online purchases?
Your credit card number and other private information are protected by encryption, which turns them into an unintelligible code. By doing this, hackers are unable to obtain your bank information while you are making transactions.
What does a website’s HTTPS stand for?
HTTPS signifies the usage of encryption (via TLS/SSL) on the webpage. By guaranteeing a secure connection between your browser and the server, it guards against data interception.
Is it still possible to hack encrypted data?
Although encryption greatly reduces the likelihood of data being compromised, it is still possible. Longer keys and robust algorithms make it far more difficult for hackers to decrypt data without permission.