Table of Contents
What is Wireless Penetration Testing?
How to perform wireless Penetration Test: Wireless pen testing is a process of cybersecurity inquiry that delivers complete info on any and all weaknesses associated to your Wi-Fi networks. It’s a deep dive into what networks occur, how influential their safety is, and what policies attach to them—and how.
Wireless penetration testing includes detecting and investigating the networks among all devices associated to the business’s Wi-Fi. These devices contain smartphones, tablets laptops and any other internet of things (IoT) devices. Wireless penetration tests are naturally executed on the client’s site as the pen tester desires to be in series of the wireless signal to contact it.
Wireless pen testing contains connectivity to devices such as:
- Laptop computers and Desktop
- Mobile devices and Tablets
- IOT (All Internet of Things) devices
How to Conduct Wi-Fi Penetration Testing
If you want to gain the profits of pen testing, one of the greatest ways is to test the waters with a wireless or Wi-Fi pen test. It’s an exclusive form of pen testing that associate together physical and virtual essentials to analyze one of the greatest helpless parts of your complete cybersecurity.
This monitor will walk over indeed how you must manage a wireless pen test, or how a constricted agency (like us) would go about leading one. That way, you know how to transmit out the process yourself, or what to assume when appointing specialized support.
Steps to Performing a Wireless Penetration Test
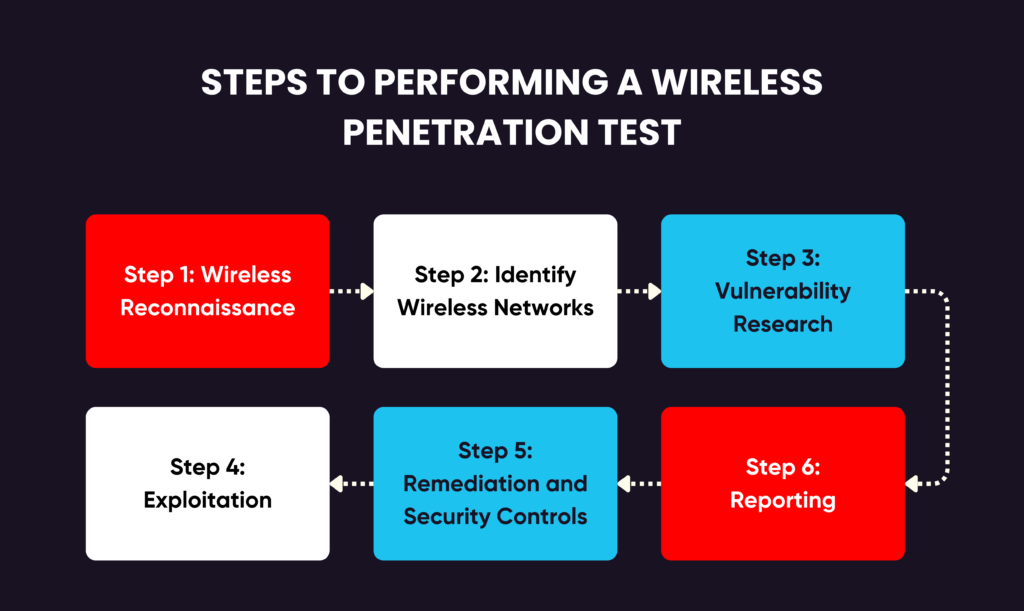
Wireless penetration testing is a critical process used to identify vulnerabilities in wireless networks, ensuring they are secure from unauthorized access and cyber threats. A structured approach is required to effectively assess security weaknesses, mitigate risks, and reinforce defenses. Below are the key steps involved in performing a wireless penetration test in detail.
Wireless Reconnaissance
Wireless reconnaissance is the initial phase where testers gather information about available wireless networks, access points, and connected devices. This step helps in identifying potential security weaknesses before attempting any exploitation. By conducting reconnaissance, penetration testers can determine network configurations, authentication protocols, and encryption types in use.
| Key Activity | Description |
| Passive Scanning | Using tools like Kismet or Wireshark to detect available networks without actively interacting with them. |
| Active Scanning | Sending probe requests using tools like Airodump-ng to gather more details about connected clients, SSIDs, and encryption types. |
| Identifying Hidden SSIDs | Capturing beacon frames to uncover hidden networks that may not be broadcasting their SSIDs. |
| Signal Strength Analysis | Determining the physical location of wireless access points using tools like Wi-Fi Pineapple. |
Identify Wireless Networks
Once reconnaissance is complete, the next step is to map and categorize the identified networks based on their security settings and configurations. Understanding network types and security implementations helps in determining potential attack vectors.
| Key Activity | Description |
| SSID Enumeration | Listing all discovered networks and their security configurations (WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA3). |
| Authentication and Encryption Analysis | Understanding the encryption types and authentication methods used. |
| Detecting Rogue Access Points | Identifying unauthorized access points that could be used for malicious activities. |
| Identifying Open Networks | Finding unsecured networks that do not require authentication. |
Vulnerability Research
After identifying the wireless networks, the next step involves researching vulnerabilities that could be exploited within the network’s security framework. This includes examining encryption weaknesses, misconfigured devices, and outdated security implementations.
| Key Activity | Description |
| Checking Weak Encryption Protocols | Identifying networks using outdated security standards like WEP or WPA. |
| Assessing Default Credentials | Detecting access points with default or weak administrator passwords. |
| Reviewing Misconfigured Devices | Identifying improperly configured network devices that could be exploited. |
| Analyzing Known Exploits | Researching common vulnerabilities using databases such as the CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) list. |
Exploitation
This phase involves attempting to exploit discovered vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to the network, devices, or data. The goal is to simulate real-world attacks to determine how resilient the network is to intrusion attempts.
| Key Activity | Description |
| Cracking Weak Passwords | Using tools like Aircrack-ng to perform dictionary or brute-force attacks on WEP/WPA encrypted networks. |
| Evil Twin Attacks | Creating a fake access point to trick users into connecting and capturing their credentials. |
| Deauthentication Attacks | Forcing legitimate users off the network to capture their re-authentication packets. |
| Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks | Intercepting network traffic to extract sensitive information. |
Remediation and Security Controls
Once vulnerabilities have been exploited and risks assessed, the next step is to implement security measures to prevent potential threats. Strengthening security controls ensures that previously identified vulnerabilities do not remain exploitable.
| Key Activity | Description |
| Upgrading Encryption Protocols | Ensuring networks use the latest security standards like WPA3. |
| Implementing Strong Authentication | Enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for wireless access. |
| Securing Access Points | Changing default credentials, disabling WPS, and enabling MAC address filtering. |
| Monitoring and Logging | Using security information and event management (SIEM) tools to track network activity and detect anomalies. |
Reporting
The final phase involves documenting findings, detailing exploited vulnerabilities, and providing recommendations for security improvements. A well-structured report enables organizations to take corrective actions effectively.
| Key Activity | Description |
| Creating a Detailed Report | Documenting identified vulnerabilities, exploitation techniques, and security risks. |
| Risk Assessment and Impact Analysis | Evaluating the severity of each vulnerability and its potential business impact. |
| Providing Security Recommendations | Suggesting actionable steps to mitigate identified risks. |
| Presenting Findings to Stakeholders | Sharing results with IT security teams and management to implement necessary fixes. |
Different Types of Pen Testing

The strongest defense starts with a proactive approach, and ethical hacking offers various offensive strategies. Wireless penetration testing is one key method used to strengthen cybersecurity. As part of the broader penetration testing framework, it focuses on assessing and securing wireless networks while complementing other targeted tests that evaluate different aspects of an organization’s cyber defenses.
All the numerous types of pen testing fall into two key categories:
- Black hat pen testing – Black hat pen testing Also called black box, in this kind of replicated attack the hacker initiates with no info delivered, reflecting actual-world unplanned attacks. This kind of testing frequently emphases on external examination
- White hat pen testing – White hat pen testing Also called white box, in this kind of pen test a hacker is delivered a exact set of prearranged info that notifies the test. In numerous circumstances white hat/box testing emphases on internal examination
In various circumstances the real test executed doesn’t fit totally into either classification. A hacker might be delivered with confident info, white hat style, but formerly also perform supplementary investigation (black hat tactic). These grey hat (or grey box) varieties might be intended upfront or they’re the significance of an on-the-fly modification on the part of the tester. In accumulation to these overall classifications of beginning informational context, additional key difference occurs among two other foremost models of penetration testing:
- External pen tests – These tests initiate from “outside” your business’s virtual and physical boundaries. They naturally emphasis on the methods a hacker can arrive into your system, as well as how rapidly and simply they can insinuate inner cogs of the network.
- Internal pen tests – In difference, internal pen testing initiates from “within” your business’s boundary. They naturally emphasis on what types of harm a hacker can do once already inside, counting how rapidly they can absolutely control your system.
Through these four main types, wireless pen tests are just one of the potentials.
Key Objectives of a Wireless Penetration Test
A professional penetration test should prioritize identifying and addressing the most easily exploitable vulnerabilities, often referred to as “low-hanging fruit.” These weaknesses pose the highest risk and require immediate attention. For Wi-Fi networks, vulnerabilities are frequently found in access points, primarily due to weak Network Access Controls and the absence of MAC filtering.
Without these essential security measures, attackers can exploit network weaknesses using various Wi-Fi hacking techniques and tools, potentially gaining unauthorized access and compromising sensitive data.
Different Types and Focus Areas of Penetration Testing
Pen tests can also emphasis on a number of other parts, or mixtures thereof, also your business’s wireless networks. The other key emphases of pen testing vary—counting both white hat and black hat (and internal or external) examination— is in accumulation to hybrid procedures.
The additional key kinds of pen testing to reflect contain:
Network service pen tests – These types of replicated attacks look at all types of networks complex in your business’s intersected systems. Moving beyond just Wi-Fi, they also inquiry into parts such as:
- IPS evasion tactics, deception vulnerabilities, and DNS-based threats
- Firewall setup strategies and software component management.
Web application pen tests – this penetration tests emphasis on web-centered applications, diving into browsers and all plugins or extensions those users trust upon to direct the internet and execute work or commercial utilities. The hacker wills emphasis on:
- CSS, HTML, cookies, error messages and Links
- Histories, content and Navigation capabilities
- User profile info payments, credentials, etc.
Social engineering pen tests – Unlike the other methods of testing well-known overhead, social engineering includes a human component. This kind of examination involves trying to cooperation a cybersecurity system over a reliable member. Illustrations contain:
Cyber threats come in many forms, including remote scams like phishing, where attackers deceive employees into revealing login credentials, allowing unauthorized system access. Physical breaches, such as fraudulent identification, can also grant intruders access to critical hardware.
To enhance security, businesses should adopt a tailored approach, blending internal and external assessments with ethical hacking techniques to create a comprehensive defense strategy.
Maximize Your Cyberdefenses with Senselearner Security
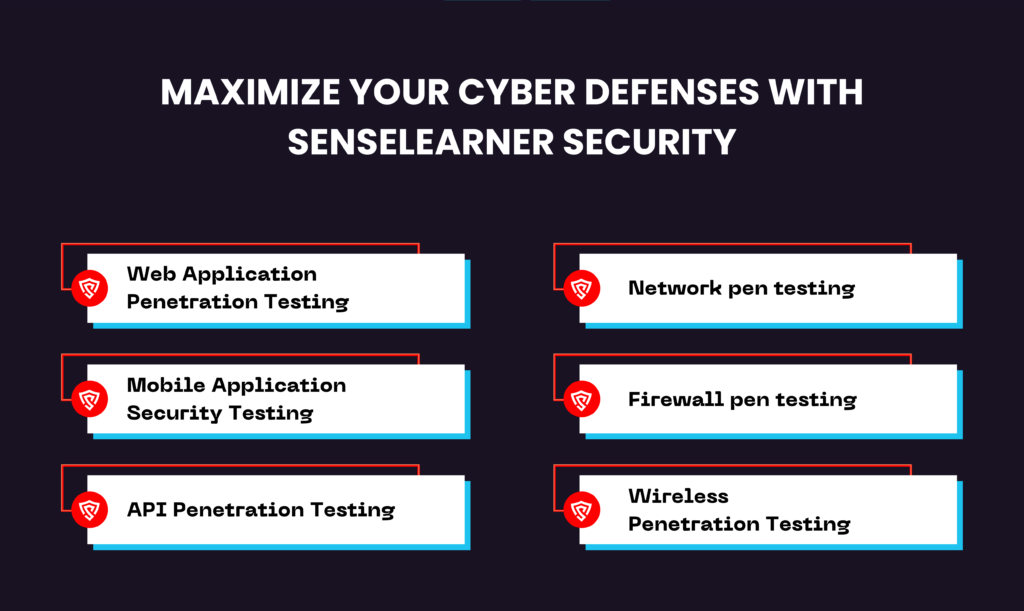
As you can see, wireless or Wi-Fi pen testing is distant from the only generous of penetration-centered cybersecurity examination your business can use to boost its Cyberdefenses. At Senselearner Security, our penetration testing facilities contain a suite of alternatives, counting but not limited to:
- Web Application Penetration Testing
- Mobile Application Security Testing
- API Penetration Testing
- Network pen testing
- Firewall pen testing
- Wireless Penetration Testing
Our goal is to provide customized cybersecurity services that align with your business needs, allowing you to choose the specific tests that best suit your security strategy. With years of industry experience, our experts adhere to the highest penetration testing standards, including PTES and other regulatory guidelines.
Beyond penetration testing, we offer comprehensive cybersecurity consulting, analysis, and solutions. Whether you need compliance support or vulnerability management, our team is here to help. Contact us today to learn more, for cybersecurity courses visit senseacademy
Explore More: 5 pillars of SaaS security: That you must know
FAQ
What are common vulnerabilities found in Wi-Fi networks?
Weak encryption (e.g., WEP or poorly configured WPA2)
Default credentials on access points
Rogue access points and unauthorized devices
Lack of MAC filtering or Network Access Controls
How can organizations secure their Wi-Fi networks?
Use strong encryption (WPA3 recommended).
Change default SSIDs and passwords.
Enable MAC address filtering and disable unused SSIDs.
Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for network access.
Regularly conduct penetration tests and audits to identify security gaps.
Who should perform a wireless penetration test?
Certified cybersecurity professionals, ethical hackers, or penetration testing teams with expertise in wireless security should conduct these tests to ensure accuracy and compliance.
How often should a wireless penetration test be conducted?
Regularly, at least once a year or whenever there are major changes in network infrastructure, new devices, or increased security threats.




One thought on “How to perform wireless Penetration Test”