Table of Contents
What Is SaaS Security?
SaaS security is a set of plans and methods intended to guard SaaS applications and the information and user characteristics they hold. These plans include safeguarding maintaining compliance with various regulations information transmission, ensuring data privacy, and managing access. SaaS security confirms that your SaaS-centered business procedures are safe, irrespective of where information is stored or how they are accessed.
Conflicting to common misunderstanding, SaaS security is not the only accountability of the service provider. As a user, you also play an important part in protecting your information. While the supplier is blamable for safeguarding the substructure and request, you are accountable for how you use the facility, counting handling contact panels and information handling processes. This article explores the five pillars of SaaS security and their importance in maintaining a secure cloud environment.
Benefits of SaaS Security
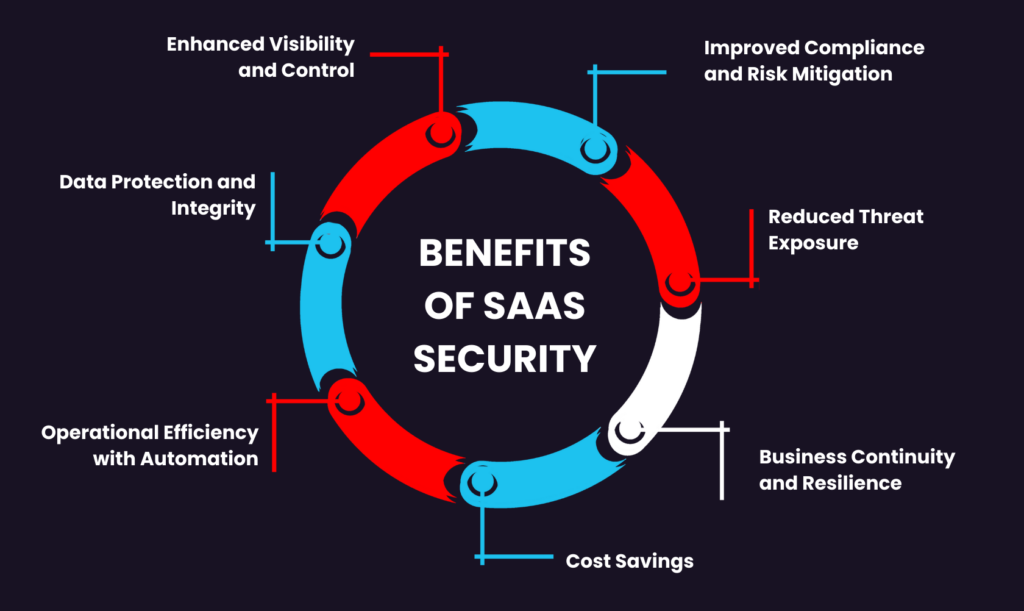
SaaS security delivers administrations with necessary security; compliance, operational efficiency and confirming data protection. Beneath are the main profits of applying a strong SaaS security outline:
Enhanced Visibility and Control
SaaS security clarifications deliver centralized visions into all requests, user action, and information flows. This reflectivity assists administrations observer contact, identify unapproved use, and confirm that all SaaS tools bring into line with safety rules.
Improved Compliance and Risk Mitigation
With regulatory necessities like GDPR and SOC 2 flattering stricter, SaaS security assists administrations uphold obedience by applying panels that address data security and privacy values, decreasing the threat of consequences or lawful significances.
Data Protection and Integrity
A robust SaaS security outline confirms the confidentiality and exactness of private information stowed or processed in SaaS requests. This decreases the likelihood of information breaches and illegal alterations, inspiring trust amongst investors.
Reduced Threat Exposure
By organizing vibrant threat discovery and behavior analytics, SaaS safety reduces threats and alleviates threats from malware, phishing and other cyber threats. This assists businesses stay forward of developing attack vectors.
Operational Efficiency with Automation
SaaS security integrates automation for procedures like incident response, compliance monitoring and access management. This updates processes, saving time and capitals while preserving a robust safety position.
Business Continuity and Resilience
SaaS security confirms nonstop processes even in the face of cyber events. Disaster rescue plans, safe data backups, and fast incident response abilities donate to industry continuity and flexibility.
Cost Savings
By averting data breaches, decreasing shadow SaaS, and enhancing request usage, SaaS safety knowingly cuts costs related with faults, consequences, and rescue efforts. These savings can be rearranged to additional invention and development.
Here are the 5 pillars of SaaS security
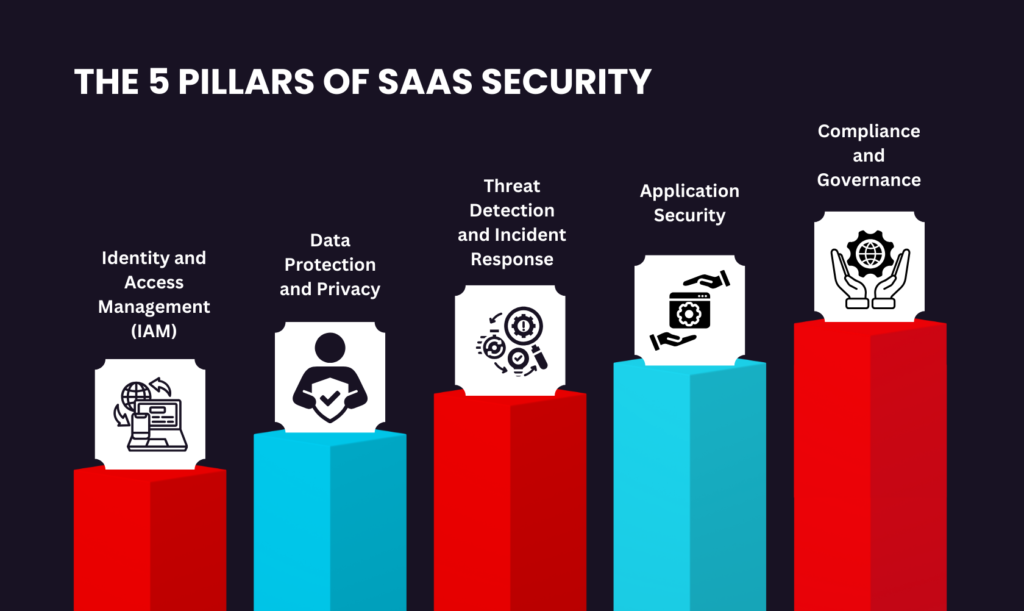
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Importance:
IAM is the foundation of SaaS security, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive systems and data. Unauthorized access can lead to data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage.
Key Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Adds an extra layer of security beyond just usernames and passwords. |
| Single Sign-On (SSO) | Simplifies user authentication while maintaining security. |
| Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) | Assigns permissions based on user roles, limiting unnecessary access. |
| User Behavior Analytics (UBA) | Monitors and detects unusual login patterns or suspicious activities. |
Data Protection and Privacy
Importance:
SaaS applications handle vast amounts of sensitive data, making data protection a top priority. Ensuring data privacy and security minimizes risks associated with data breaches, regulatory non-compliance, and cyber threats.
Key Components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Protects data at rest and in transit using strong encryption protocols. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Monitors and prevents unauthorized data access or transfer. |
| Data Masking and Tokenization | Helps anonymize sensitive information to prevent exposure. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adheres to frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA to ensure data privacy. |
Application Security
Importance:
Securing SaaS applications prevents vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. Poorly secured applications can lead to security breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Key Components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) | Incorporates security practices in every phase of development. |
| Penetration Testing | Regular testing to identify and fix vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them. |
| Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) | Protect applications from threats like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). |
| API Security | Ensures secure communication between SaaS applications and external services. |
Threat Detection and Incident Response
Importance:
Threat detection and incident response mechanisms help organizations proactively identify and mitigate security risks before they cause significant harm.
Key Components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Collects and analyzes security event logs for threat detection. |
| Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) | Monitors network traffic for suspicious activities and blocks malicious threats. |
| Automated Incident Response | Uses AI-driven tools to respond to threats in real-time. |
| Continuous Monitoring | Provides ongoing surveillance of security environments to detect anomalies. |
Compliance and Governance
Importance:
Compliance and governance ensure that SaaS providers and users adhere to industry standards and regulations. It helps businesses maintain transparency, accountability, and trust with customers and stakeholders.
Key Components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Aligns with legal frameworks like SOC 2, ISO 27001, GDPR, and PCI-DSS. |
| Risk Management | Identifies and mitigates potential security risks through audits and assessments. |
| Audit Logs and Reporting | Maintains detailed records of user activities for security analysis. |
| Policy Enforcement | Ensures security policies are consistently applied across the organization.5 pillars of SaaS security |
Essential SaaS Security Best Practices
After establishing the five pillars, implementing best practices can assists increase the safety position of your SaaS applications and decrease the threat to business processes.
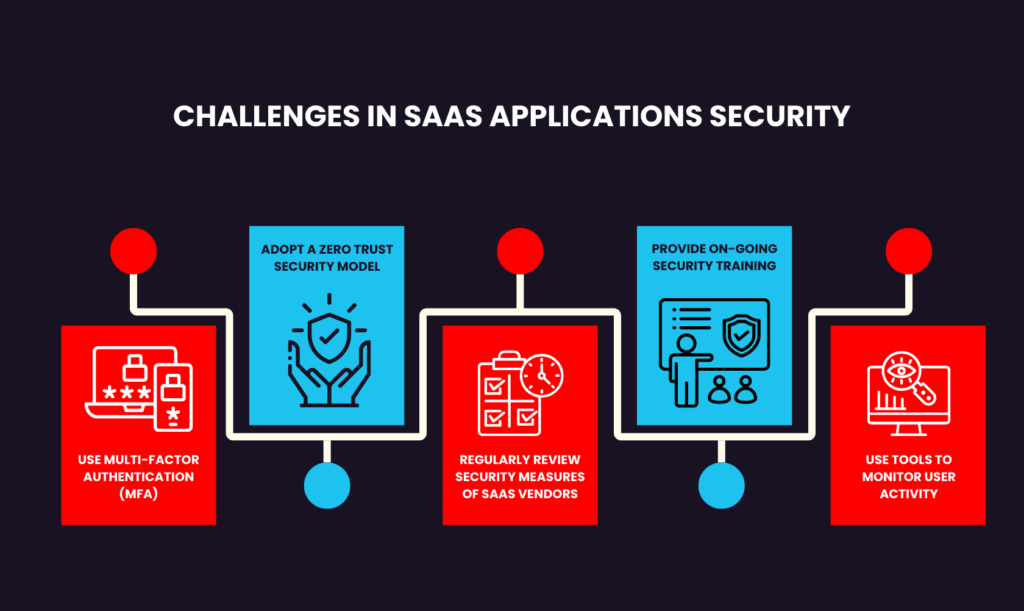
Use Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA needs users to deliver at least two forms of ID before allowing contact to your SaaS applications. This could be something they are (such as fingerprint), something they have (such as mobile device) or knowledge based (such as password).
MFA (Multi-factor Authentication) delivers an additional layer of safety, making it tougher for unapproved users to increase contact even if they crack one verification issue. It’s mainly helpful for defending private information and high-risk processes.
Regularly Review Security Measures of SaaS Vendors
The strength of your SaaS security depends on the most vulnerable point in your supply chain. Hence, it’s vital to frequently audit the safety rules and methods of your SaaS dealers. This includes measuring their compliance status, incident response procedures and data protection capabilities.
To facilitate this procedure, reflect initial a vendor risk managing program. This can assists you implement appropriate mitigation methods, prioritize risks and detection potential vulnerabilities.
Provide On-going Security Training
Human mistake and absence of safety consciousness are amongst the most mutual reasons of safety breaches. This means on-going training to your employees is a serious SaaS security best practice.
This training should teach your crew on the newest cyber threats, safe online behaviors, and your administration’s safety rules and processes. It should also underline the significance of their part in preserving SaaS security and inspire them to report any doubtful actions.
Use Tools to Monitor User Activity
Observing user action on your SaaS applications is another operative way to boost your safety. This includes following and analyzing activities like file downloads data modifications and logins.
User action observing tools can deliver visions into rare behaviors, possible safety events, and obedience violations. They can also assists detect production bottlenecks and progress user knowledge.
Adopt a Zero Trust Security Model
Lastly, reflect accepting the zero trust models for your SaaS security. This method undertakes that any user or device, whether inside or external your network, could be a possible risk. So it needs harsh identity confirmation for every person and device trying to contact your systems, irrespective of their location.
The zero trust simulations can deliver strong defense beside numerous cyber threats, counting insider attacks and progressive determined risks. It can also assist information security in the cloud and support obedience with data privacy rules.
Challenges in SaaS Applications Security
Data Security
Data security is an important concern in SaaS applications. Additional so than in traditional, on-evidence requests, there is a risk of data breaches, also from exterior hackers or interior risks. Moreover, data communication among your local system and the SaaS application can be interrupted, leading to data contact.
Data Ownership and Control
With SaaS, your data is stowed in the supplier’s servers. This condition can lead to doubts over data proprietorship and panel. Who has contact to your data? Can the supplier operate it? Administrations using SaaS applications must demeanor due diligence to get solutions to these queries and plans their safety plan accordingly.
Integration Issues
Most businesses use numerous SaaS requests, each with their safety procedures and values. In similar, there are also on-premise requests and legacy systems. Connecting these different systems can be challenging and May create security vulnerabilities if not implemented properly. Considerably, many administrations absence visibility over SaaS requests and their information flow.
Compliance and Regulatory Concerns
Compliance with data protection rules and business values is a dangerous worry for businesses in almost every business. It is vital to confirm that SaaS suppliers obey with the related rules and values. Even if they are, administrations using SaaS requests must regulate and transmit out their own obedience duties.
Vendor Lock-in
Vendor lock-in mentions to the trouble of transferring from one SaaS supplier to additional. If you choose to change suppliers, you may face tasks in transferring your information. Incapability to transfer information makes a variety of business threats, and even if movement is probable, the movement procedure itself can uncover your information to attacks.
Downtime and Service Interruptions
Finally, downtime and service interruptions can affect the accessibility of your information and facilities. This can lead to efficiency losses and client disappointment. In some cases, SaaS supplier faults and facility matters could outcome in information loss or contact to safety vulnerabilities.
Explore More: Top 10 API Testing Tools: Importance and Features
FAQ
What role does Application Security play in SaaS security?
Application Security helps protect SaaS platforms from vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and unauthorized API access.
How does Compliance & Governance affect SaaS security?
Compliance ensures that SaaS applications follow industry standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001, helping businesses avoid legal risks.
Why is Security Monitoring & Incident Response essential for SaaS?
Continuous monitoring detects threats in real-time, while incident response helps mitigate attacks quickly to minimize damage and downtime.
How can businesses improve their SaaS security posture?
Businesses should implement multi-factor authentication (MFA), data encryption, security audits, and employee training to strengthen SaaS security.