Table of Contents
Our everyday lives are greatly impacted by mobile applications, which facilitate tasks like banking, internet shopping, medical care, and entertainment. These apps handle enormous volumes of private financial and personal data, and millions of users depend on them. Any mobile app security weakness has the potential to cause identity theft, data breaches, and large financial losses. The technique of carefully analyzing programs to find flaws before they can be exploited is known as mobile app security testing. Businesses may preserve user trust and fortify their apps against hackers by conducting this testing.
What is Mobile App Security Testing?

The process of checking and addressing security flaws that hackers can exploit is known as mobile app security testing. Apps are tested to ensure they can withstand threats such as hacking attempts, data leaks, and other cyberthreats. Because mobile devices are frequently less secure than desktop PCs, fraudsters find them to be attractive targets. A mobile app hack can result in financial losses, information theft, and major damage to a company’s brand. Strong security measures are therefore essential for safeguarding a company and its clients as well as for technology.
Also read https://senselearner.com/top-10-cyber-security-threats/
How to Perform Mobile App Security Testing ?
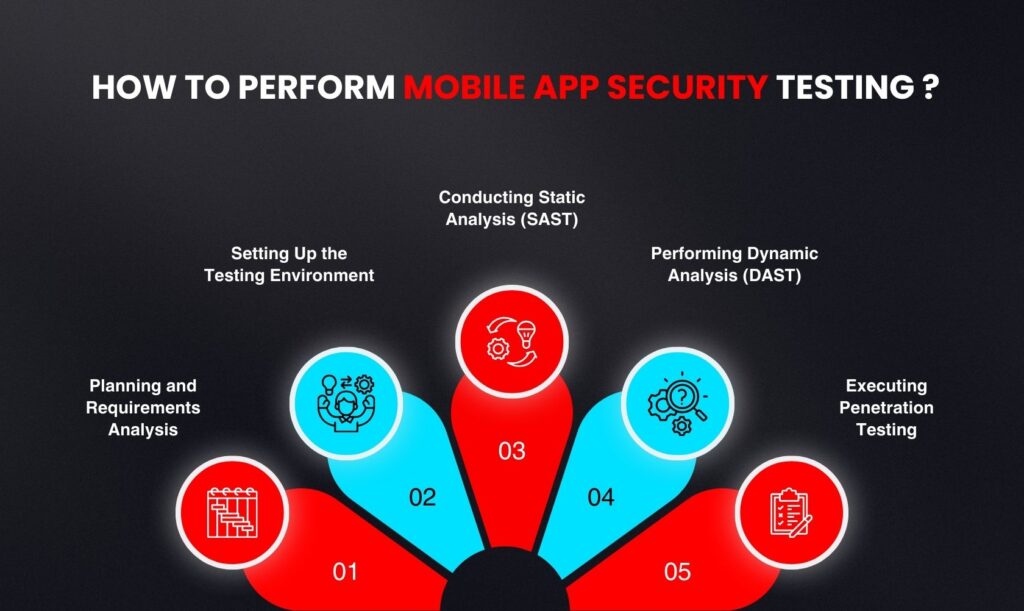
1- Planning and Requirements Analysis
The first step in mobile app security testing is to clearly define the goals and scope, which involves identifying which components—such as backend servers, APIs, or third-party integrations—will be tested, identifying sensitive data and important features that require protection, and establishing objectives like protecting user information, guaranteeing safe transactions, and adhering to regulations. Understanding the app’s architecture is equally crucial. This includes charting the data flow across the app, identifying platform-specific changes for iOS, Android, and other platforms, and checking all external libraries, SDKs, and APIs for potential vulnerabilities.
2- Setting Up the Testing Environment
In order to test in many situations, begin your preparation for mobile app security testing by using both emulators and real devices. Including rooted or jailbroken devices is also helpful in order to observe how the application functions in the event that the device is compromised. Next, test the app in various network scenarios, such as 3G, 4G, Wi-Fi, or even without internet, and configure network settings by checking and analyzing data flow using tools like Burp Suite or OWASP ZAP. Get access to the app’s source code if you can so you may thoroughly examine and test it. Verify that all testing is permitted and lawful before beginning.
3- Conducting Static Analysis (SAST)
To detect security flaws in the code, use automated code scanning tools such as MobSF, SonarQube, or Fortify as well. Verify configuration files like Info.plist and AndroidManifest.xml for errors or dangerous settings. Examine key code sections by hand, such as data handling, encryption, authorization, and authentication. Check for cryptographic keys, passwords, and API keys—all examples of hardcoded secrets. Examine for typical security issues such as OS command injection, SQL injection, and other defects related to code injection. Check to make sure the gadget is not storing critical information in an unsafe manner.
4- Performing Dynamic Analysis (DAST)
Dynamic analysis involves testing the application in real time to observe how it responds to both normal and unusual scenarios. Check if it can block incorrect or damaging inputs by looking at how it handles them. Use proxy tools to monitor the app’s network activities and make sure SSL/TLS is operating properly to protect data. To check whether a session is protected, attempt to take control of it. Also, ensure that session tokens expire when you log out or after no further use. In real time, this keeps the software safe for users.
Also read Top 10 mobile app security threats
5- Executing Penetration Testing
Pretending to attack the application in order to identify security flaws is known as penetration testing. Like a true hacker, the tester in black box testing has no idea how the application functions. Gray box testing helps uncover more hidden issues because the tester has some knowledge of the application. Tools such as Metasploit are used to test known vulnerabilities, and testers attempt to gain more access than is necessary. This involves verifying things like intents, activities, and exported app components on Android.
Visit https://circleci.com/blog/mobile-app-security-testing/
CONCLUSION
Mobile app security testing is now a must in today’s digital world; it is no longer a choice. Organizations may safeguard sensitive user data, guarantee regulatory compliance, and uphold trust by methodically planning, testing in a variety of situations, evaluating code, keeping an eye on runtime behavior, and modeling real-world threats. In a mobile ecosystem that is becoming more and more vulnerable to threats, a proactive security approach not only stops breaches but also boosts brand reputation.
What distinguishes standard web application security testing from mobile app security testing?
Mobile app testing must take into consideration platform-specific risks (iOS vs. Android), device-level security settings, offline storage, and mobile-specific APIs—elements that are sometimes missing from standard web app testing—even though both seek to detect and address vulnerabilities.
After the initial testing stage, how can businesses guarantee continued security for mobile apps?
Integrating testing into CI/CD pipelines, doing recurring penetration tests, keeping an eye out for new threats, quickly implementing security patches, and educating development teams on secure coding techniques are all necessary for continuous security.
What are the limitations of completely automated mobile app security testing?
Human-led manual testing and threat modeling are crucial because, although automation technologies can identify many problems rapidly, they frequently overlook intricate logic errors, business rule infractions, and sophisticated attack pathways.



One thought on “Mobile App Security Testing, What is it & How to perform it ”