Businesses in today’s digital era mostly depend on networks to handle operations, store data, and connect with team members spread across different locations. Although this reliance increases productivity and speed, it also creates significant risks like data theft, phishing, and hacking. Organizations use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to reduce these risks. By creating a secret, encrypted tunnel between the user and the internet, a VPN significantly improves the security of online communication. VPNs offer an extra level of protection and guarantee that company data stays private, even while using public or untrusted networks, by hiding essential data from unauthorized users.
Table of Contents
What are VPNs?

A virtual private network, or VPN, is a security tool used to maintain the privacy and security of internet connections. It reroutes data through a secure server that serves as a barrier rather than delivering it in a transparent way. It is more difficult for anyone to trace activity or location when this server hides the user’s true IP address. All data passing via the VPN is encrypted at the same time, making it difficult to read or steal. Because of this, VPNs are particularly useful for companies that handle sensitive data, such as financial information, client information, or contracts.
Importance of VPNs in Business Security
VPNs are essential for safeguarding business networks and ensuring safe communication. Their significance can be highlighted as follows:
Protection From Cyberthreats: Business networks are at risk from malware, phishing, and hacking. VPNs protect private information by encrypting it, making it unusable by hackers.
Safe Remote Access: Employees who operate remotely can safely access corporate systems without disclosing confidential company data to untrusted or public networks.
Data privacy: Virtual private networks (VPNs) protect private files, customer information, and financial records from strangers.
Support for Compliance: Many businesses require strict data protection regulations to ensure compliance. VPNs assist companies in fulfilling these legal responsibilities.
Reputation security: Trust is damaged by data leaks. VPNs lower these dangers, safeguarding a business’s reputation and brand image.
How Does a VPN Work?
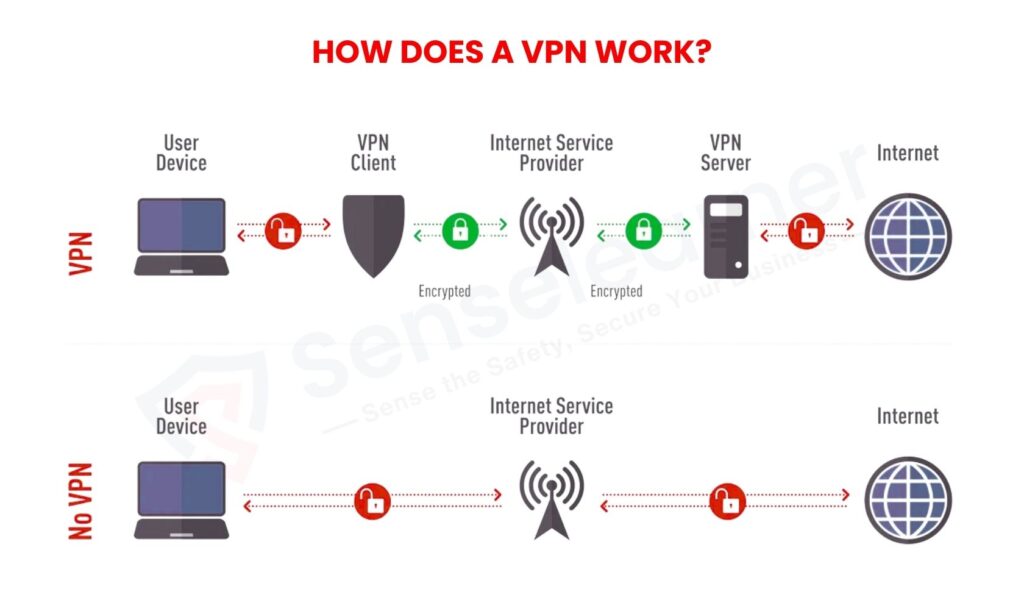
A VPN connects a device to the internet by establishing a secure “tunnel.” When a user joins via a VPN, the data is first sent to a VPN server, which encrypts it before sending it on. Anyone attempting to intercept the data cannot read it because of the encryption. Additionally, the VPN server’s address is used to hide the user’s real IP address. This procedure guarantees: Communication that is encrypted for privacy.
IP address hidden in order to prevent tracking.
Browsing securely across public or unreliable networks.
How VPNs Protect Data and Communication?
One of a VPN’s most crucial functions is data and communication protection. Every message, file, and email that travels through a VPN is encrypted, making it impossible for hackers to read or use even if they manage to intercept it. Additionally, VPNs hide the user’s true IP address, making it more difficult for third parties to determine their location or identity. This guarantees the privacy and security of critical activities, including file sharing, financial transactions, and video conferences. Important safeguards consist of:
Encryption: Using powerful algorithms, data is transformed into unintelligible code, shielding it from hackers and unwanted access.
IP masking: It protects the user’s device, location, and true identity from online dangers by hiding their original IP.
Safe Transfers: When files, documents, and messages are transferred across public or unreliable networks, there is a lower chance of interception.
VPNs are a reliable option for protecting critical business activities and securing corporate communication because of these capabilities.
VPNs in Remote Work and Hybrid Environments
As remote and hybrid work become more common, it is more crucial than ever to have safe access to company resources. Workers who use public Wi-Fi networks, coworking spaces, or their homes are more vulnerable to cyberattacks. This problem is resolved by VPNs, which offer a safe way to access the business’s internal network from anywhere. This guarantees that data remains secure regardless of the location from which employees check in. VPNs also make it possible for companies with offices in different areas to collaborate easily and securely. Remote work settings would put businesses at serious danger and make corporate communication highly vulnerable in the absence of VPNs.
Key Benefits of Using VPNs in Corporate Networks
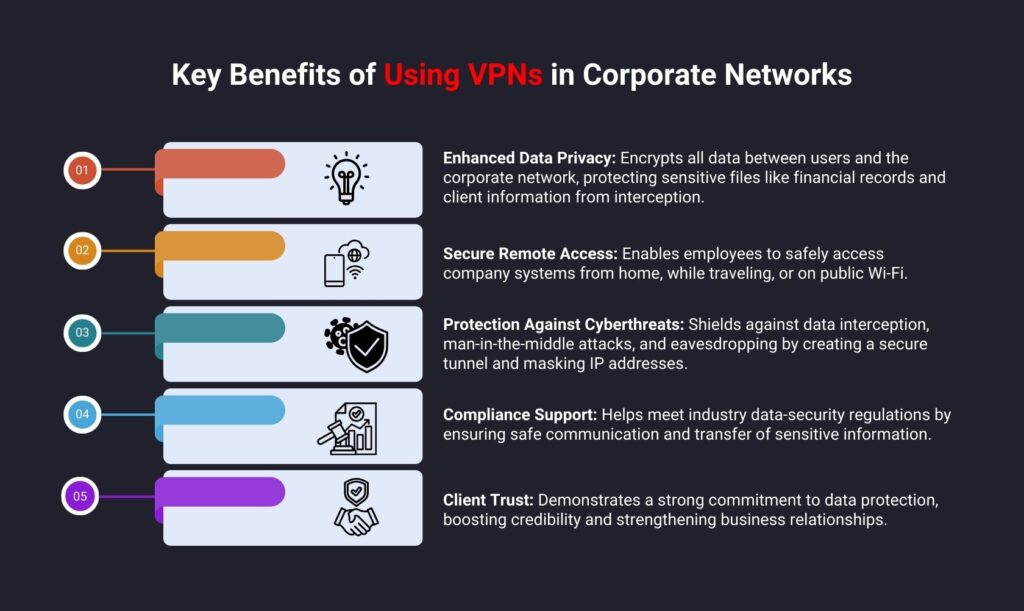
Businesses may maintain safe, effective, and reliable operations by utilizing virtual private networks (VPNs) in corporate networks. VPNs are an essential part of corporate network security because of the benefits, which help businesses protect data, allow remote work, and preserve trust in digital operations.
Enhanced Data Privacy: All data sent between users and the corporate network is encrypted via VPNs. This guarantees the confidentiality of important business data, including internal documents, financial information, client records, and strategic plans. Even in the event that hackers manage to intercept the data, encryption shields the business from possible financial and brand damage.
Secure Remote Access: Whether working from home, on the go, or via public Wi-Fi, staff members may securely access company systems from any location. VPNs offer a secure connection, lowering the possibility of data breaches or illegal breaches while protecting all communications, file transfers, and system access.
Protection Against Cyberthreats: VPNs help in defending against a range of cyberthreats, such as data interception, man-in-the-middle assaults, and eavesdropping efforts. VPNs make it harder for hackers to identify users or obtain private data by establishing a secure tunnel and hiding IP addresses. This gives the company network a vital extra layer of security.
Compliance Support: Strict data security laws and compliance requirements apply to a wide range of sectors. By protecting communications and guaranteeing the safe transmission of sensitive data, VPNs assist enterprises in meeting these standards. This shows the company’s dedication to data protection and lowers the possibility of legal repercussions.
Client Trust: Employing VPNs shows customers and business associates that the organization takes data security seriously. Relationships are strengthened and trust is increased when sensitive data is managed sensibly and safely. This is crucial for preserving long-term company success and credibility in cutthroat marketplaces.
How Can VPNs Enhance Network Security?
VPNs greatly increase network security by lowering the possibility of data leaks and cyberattacks. They establish a safe environment in which firm resources are only accessible by authorized individuals. This lowers the possibility of hackers breaking into the system. VPNs also safeguard connections on public Wi-Fi networks, which are common targets for data theft attempts by fraudsters. Additionally, they help companies stay out of trouble with the law by promoting compliance with international data security standards. VPNs serve as a barrier that fortifies the entire business network against frequent cyberthreats by encrypting traffic, hiding IP addresses, and limiting access.
Types of VPNs
VPNs are made to satisfy various corporate requirements, and selecting the right type guarantees proper network security. Businesses may ensure secure communication and data protection across all devices and locations by choosing the VPN solution that best suits their size, structure, and workflow by being aware of these types. The primary types of VPNs include
Remote Access VPN: This type of connection safely links a worker’s device to the internal network of the business. For remote professionals who require access to files, emails, or programs from public Wi-Fi networks, hotels, or their homes, it is perfect. By encrypting data and hiding the user’s IP address, the VPN stops hackers from obtaining private information. It is easy to set up and effective for small groups or individuals that require safe access from any location.
Mobile VPN: Mobile VPNs are made for devices that move between networks a lot, like field workers’ or traveling employees’ mobile phones, laptops, or tablets. Mobile VPNs, compared to traditional VPNs, provide a steady, secure connection even when the device switches between Wi-Fi, cellular, and other networks. This guarantees constant access to data and business apps without sacrificing security. Businesses with workers that are constantly on the road, delivery services, or sales teams who require secure network access from any location would find mobile VPNs very helpful.
Site-to-Site VPN: This type of VPN connects whole workplace networks, frequently across nations or towns. It enables safe online communication between a company’s many offices, just like if they were connected to the same local network. For big businesses with branch offices, site-to-site VPNs are crucial because they guarantee secure data exchange, centralized administration, and uniform security standards everywhere. Workers from several offices can use common resources without being concerned about outside dangers.
VPNs vs. Other Security Tools
VPNs are effective, but there are other security measures out there as well. Antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and firewalls all have distinct functions. Intrusion detection systems keep an eye on questionable activity, firewalls prevent unwanted access, and antivirus programs identify and eliminate dangerous files. VPNs, however, protect the actual communication channel. This indicates that as part of a multi-layered security strategy, VPNs function best when used in conjunction with other solutions. Companies that use these tools together with VPNs strengthen their defenses against cyberattacks and lower the risk of depending on just one security solution.
Best Practices for Implementing VPNs in Companies
In order to maintain reliable safety, businesses need to adhere to a set of best practices for VPNs to be effective. By following these practices, VPNs are guaranteed to continue being an effective defense, safeguard private information, and improve overall network security for businesses.
Strong Encryption: Choose VPN services that use cutting-edge encryption techniques, which make intercepted data unreadable. This guarantees that private business data is safeguarded even when it travels over open networks.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): To ensure that only authorized users can log in, include additional verification procedures like biometric checks or codes delivered to mobile devices.
Frequent Updates: To fix security flaws and preserve connectivity with other security solutions, keep servers and VPN software updated.
Access Control: Set different authorization levels for various positions and limit VPN access to only those employees who require it. Employee Training: To prevent human error from compromising network security, train employees on how to use a VPN correctly, create secure passwords, and identify possible risks.
Are There Alternatives to VPNs for Allowing Employees to Work Remotely?
VPNs are still a popular way to access information securely from a distance, but new technologies provide more scalable and adaptable solutions. These substitutes are made to satisfy the security requirements of modern hybrid and cloud-based work settings. Important choices consist of:
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): ZTNA verifies each user and device before allowing access, in contrast to VPNs, which presume that everyone within the network is trustworthy. It ensures that even internal devices must adhere to security rules before connecting by taking a strict “never trust, always verify” approach.
Software-Defined Perimeter (SDP): SDP only allows access to verified users or devices and conceals network resources from unauthorized users. As a result, it is much harder for attackers to locate or take advantage of key enterprise systems, hence decreasing the attack surface.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE): SASE is a cloud-based platform that integrates security and network connection. With capabilities like firewall security, secure web gateways, traffic inspection, and identity verification, it enables safe access for workers wherever they may be.
FAQ’s
How can companies successfully use VPNs?
Businesses should implement strong encryption techniques to secure all sent data in order to use VPNs efficiently. To guarantee that only authorized users are granted access, multi-factor authentication needs to be activated. Regularly upgrading VPN software and servers is crucial to fix vulnerabilities. Employee responsibilities should determine access levels, and staff members should receive training on how to use a VPN correctly, create secure passwords, and identify security risks.
Are VPNs appropriate for big businesses?
Yes, large enterprises can benefit much from VPNs. Site-to-Site VPNs make it possible for several office sites to connect safely online, guaranteeing reliable security and simple resource sharing. Field teams, traveling staff, and remote workers may all connect securely with the use of mobile VPNs and remote access. When these technologies are used in combination, big businesses may safely accommodate a distributed workforce, preserve critical data, and protect data privacy.
How can companies successfully use VPNs?
Strong encryption techniques can be used by businesses to effectively use VPNs and safeguard data while it is being transmitted. The network can only be accessed by authorized users because of multi-factor authentication. To address vulnerabilities, VPN servers and software should be updated on a regular basis. Employee responsibilities should determine access restrictions, and staff members need to receive training on how to use a VPN correctly, create secure passwords, and spot security risks. By doing these actions, security and dependability are increased.
Conclusion
VPNs are an essential part of corporate network security because they give companies a dependable means of safeguarding private information and preserving secure routes of communication. Whether working from home, the office, or other remote locations, they guarantee that staff members may securely access corporate networks and exchange information. VPNs lower the danger of cyberattacks, data breaches, and unwanted access by encrypting data, hiding IP addresses, and building secure tunnels. In today’s digital environment, VPNs assist businesses in preserving privacy, adhering to legal requirements, and fostering trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders when used in combination with other security technologies like firewalls and antivirus software and set up according to best practices.